The December 31 Balance Sheet of the Gemco Llp Reads as Follows.
What is the Residue Canvass?
The balance sheet is one of the iii fundamental fiscal statements and is key to both financial modeling and bookkeeping. The residue sail displays the company'south full avails and how the avails are financed, either through either debt or disinterestedness. It can also be referred to as a statement of cyberspace worth or a statement of financial position. The balance canvas is based on the central equation: Avails = Liabilities + Equity.
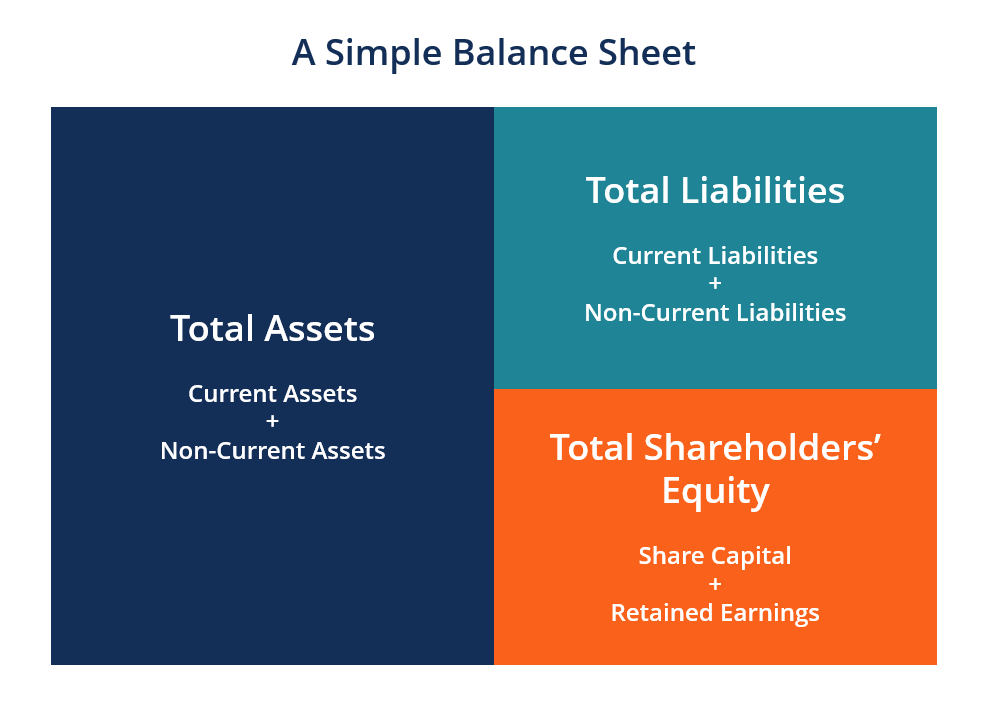
Image: CFI's Financial Analysis Course
Equally such, the residue canvass is divided into two sides (or sections). The left side of the balance sheet outlines all of a company'due south assets . On the correct side, the rest sheet outlines the company'southward liabilities and shareholders' disinterestedness .
The assets and liabilities are separated into two categories: current asset/liabilities and non-current (long-term) assets/liabilities. More liquid accounts, such as Inventory, Cash, and Trades Payables, are placed in the current section before illiquid accounts (or not-current) such every bit Plant, Belongings, and Equipment (PP&E) and Long-Term Debt.
Balance Sheet Example
Beneath is an case of Amazon's 2017 residue sail taken from CFI's Amazon Instance Study Course. As you lot volition see, it starts with current assets, then non-electric current assets, and total assets. Below that are liabilities and stockholders' disinterestedness, which includes current liabilities, not-current liabilities, and finally shareholders' equity.
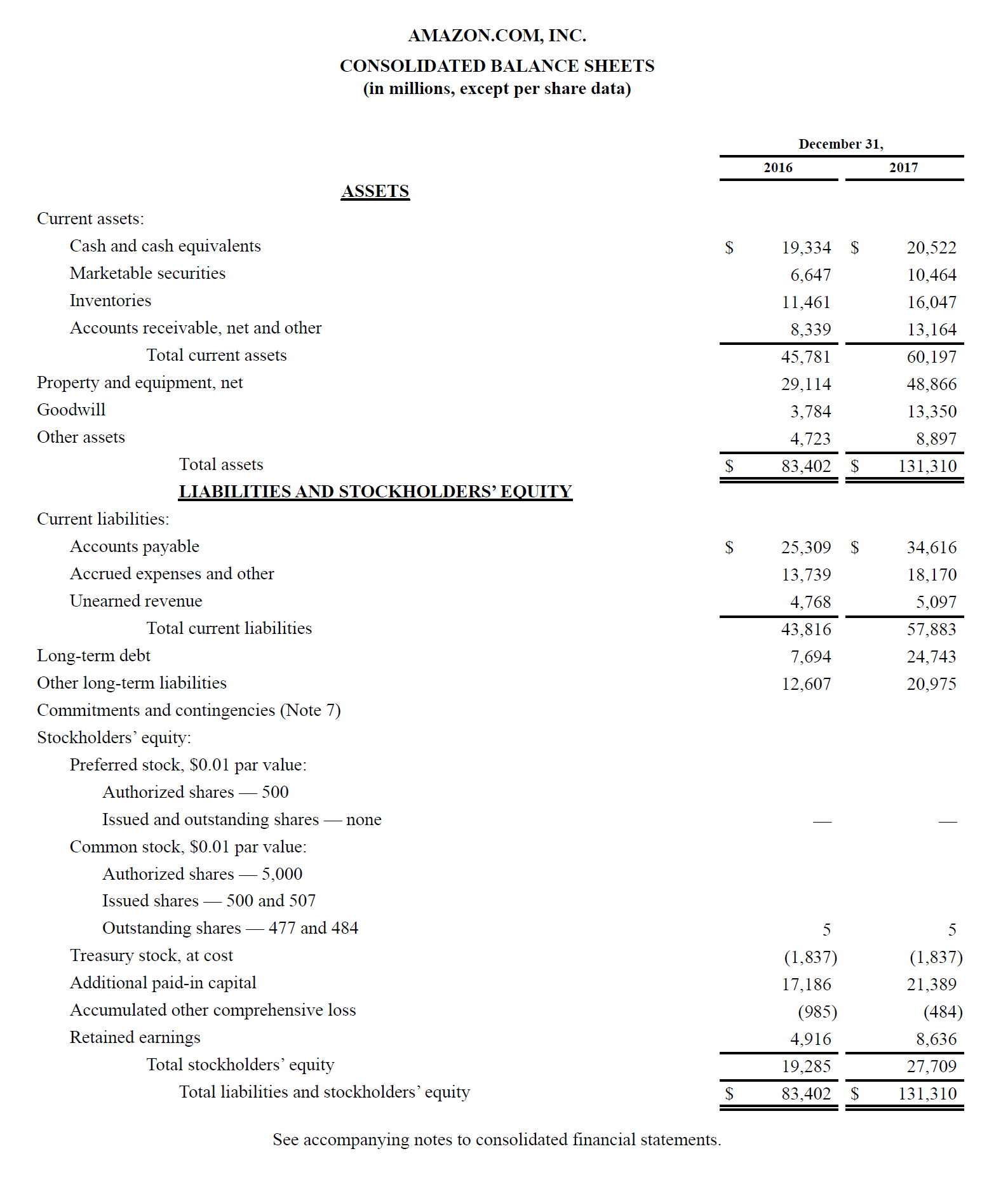
View Amazon'due south investor relations website to view the full balance sheet and almanac written report.
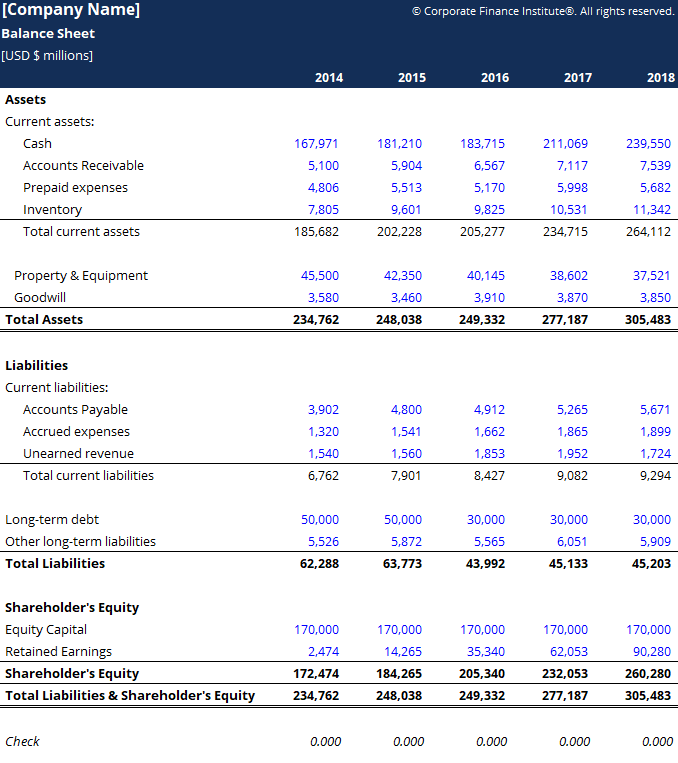
Download the Costless Template
Enter your name and email in the form below and download the free template at present! You tin use the Excel file to enter the numbers for whatever visitor and proceeds a deeper agreement of how balance sheets work.
How the Balance Sheet is Structured
Balance sheets, similar all fiscal statements, volition have minor differences between organizations and industries. All the same, in that location are several "buckets" and line items that are almost e'er included in common balance sheets. Nosotros briefly go through commonly plant line items under Electric current Avails, Long-Term Assets, Current Liabilities, Long-term Liabilities, and Equity.
Learn the basics in CFI's Complimentary Bookkeeping Fundamentals Course.
Current Assets
Cash and Equivalents
The near liquid of all assets, cash, appears on the showtime line of the residuum sheet. Cash Equivalents are likewise lumped under this line item and include assets that have brusque-term maturities nether iii months or assets that the company can liquidate on brusk detect, such as marketable securities . Companies will generally disclose what equivalents information technology includes in the footnotes to the balance sheet.
Accounts Receivable
This business relationship includes the balance of all sales revenue still on credit, net of whatsoever allowances for doubtful accounts (which generates a bad debt expense). As companies recover accounts receivables, this account decreases, and cash increases past the same amount.
Inventory
Inventory includes amounts for raw materials, work-in-progress goods, and finished goods. The company uses this business relationship when it reports sales of goods, generally under cost of goods sold in the income argument.
Non-Current Avails
Plant, Property, and Equipment (PP&E)
Belongings, Constitute, and Equipment (also known every bit PP&E) capture the company's tangible fixed assets. The line item is noted net of accumulated depreciation. Some companies volition class out their PP&E by the different types of assets, such as Land, Building, and various types of Equipment. All PP&E is depreciable except for Land.
Intangible Avails
This line detail includes all of the visitor's intangible fixed assets, which may or may not be identifiable. Identifiable intangible assets include patents, licenses, and surreptitious formulas. Unidentifiable intangible assets include brand and goodwill.
Current Liabilities
Accounts Payable
Accounts Payables, or AP, is the amount a company owes suppliers for items or services purchased on credit. As the company pays off its AP, it decreases along with an equal amount subtract to the cash account.
Current Debt/Notes Payable
Includes non-AP obligations that are due inside one year's fourth dimension or inside one operating cycle for the visitor (whichever is longest). Notes payable may also have a long-term version, which includes notes with a maturity of more i year.
Current Portion of Long-Term Debt
This account may or may non be lumped together with the above account, Electric current Debt. While they may seem similar, the current portion of long-term debt is specifically the portion due within this year of a piece of debt that has a maturity of more than one year. For case, if a company takes on a bank loan to be paid off in 5-years, this account will include the portion of that loan due in the next twelvemonth.
Not-Current Liabilities
Bonds Payable
This account includes the amortized corporeality of whatever bonds the company has issued.
Long-Term Debt
This business relationship includes the total amount of long-term debt (excluding the current portion, if that account is present under current liabilities). This account is derived from the debt schedule , which outlines all of the company'south outstanding debt, the interest expense, and the master repayment for every period.
Shareholders' Equity
Share Capital letter
This is the value of funds that shareholders have invested in the company. When a company is first formed, shareholders will typically put in greenbacks. For instance, an investor starts a company and seeds it with $10M. Cash (an asset) rises by $10M, and Share Majuscule (an equity account) rises by $10M, balancing out the balance sheet.
Retained Earnings
This is the total amount of cyberspace income the visitor decides to go along. Every period, a company may pay out dividends from its net income. Any amount remaining (or exceeding) is added to (deducted from) retained earnings.
How is the Balance Sheet used in Fiscal Modeling?
This statement is a cracking mode to clarify a visitor's financial position . An analyst tin can generally use the balance sheet to calculate a lot of financial ratios that help decide how well a visitor is performing, how liquid or solvent a visitor is, and how efficient it is.
Changes in rest canvass accounts are also used to calculate cash menses in the cash flow statement . For example, a positive modify in plant, holding, and equipment is equal to uppercase expenditure minus depreciation expense. If depreciation expense is known, capital expenditure tin can be calculated and included as a cash outflow under greenbacks menses from investing in the cash catamenia argument.
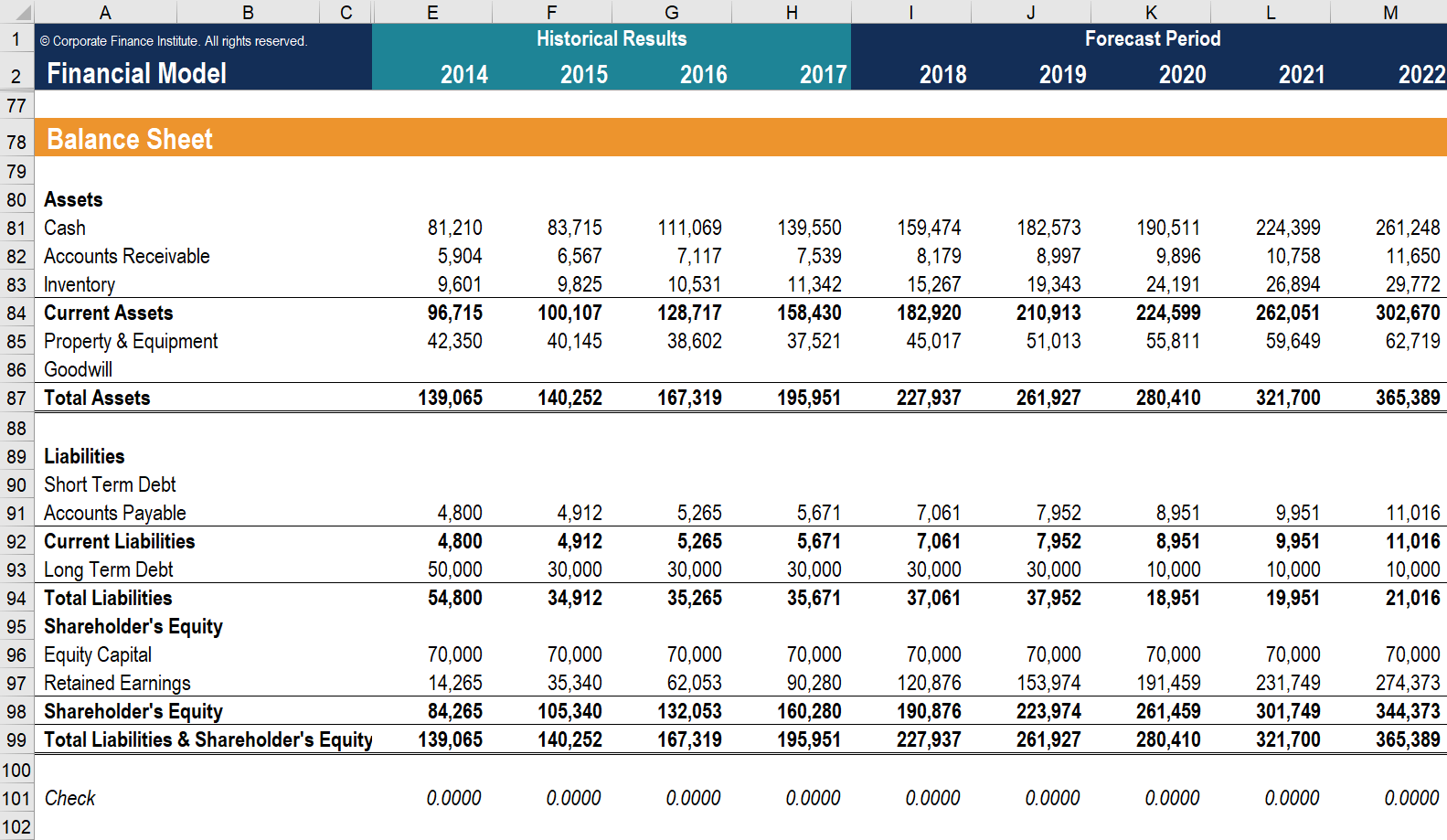
Screenshot from CFI's Financial Analysis Form.
Importance of the Balance Sheet
The rest sheet is a very important financial argument for many reasons. It tin can exist looked at on its ain and in conjunction with other statements similar the income argument and greenbacks flow statement to go a full picture of a visitor'south health.
Four important financial operation metrics include:
- Liquidity – Comparing a company'southward electric current assets to its current liabilities provides a picture of liquidity. Current assets should be greater than current liabilities, so the visitor can encompass its brusque-term obligations. The Current Ratio and Quick Ratio are examples of liquidity financial metrics.
- Leverage – Looking at how a company is financed indicates how much leverage it has, which in turn indicates how much financial risk the company is taking. Comparing debt to equity and debt to total capital are common means of assessing leverage on the balance sheet.
- Efficiency – By using the income statement in connection with the balance sheet, information technology'south possible to assess how efficiently a company uses its avails. For case, dividing revenue by the boilerplate full assets produces the Asset Turnover Ratio to indicate how efficiently the company turns avails into acquirement. Additionally, the working capital cycle shows how well a company manages its cash in the curt term.
- Rates of Return – The balance sail can be used to evaluate how well a company generates returns. For case, dividing net income by shareholders' equity produces Return on Equity (ROE), and dividing net income by total avails produces Return on Assets (ROA), and dividing internet income by debt plus equity results in Return on Invested Capital (ROIC).
All of the higher up ratios and metrics are covered in item in CFI'southward Financial Analysis Course.
Video Explanation of the Balance Sheet
Below is a video that speedily covers the key concepts outlined in this guide and the main things you need to know about a remainder sheet, the items that brand it up, and why information technology matters.
Equally discussed in the video, the equation Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders' Equity must always be satisfied!
Acquire More About the Financial Statements
To continue learning and advancing your career as a financial annotator, these additional CFI resources will be helpful:
- Income Statement
- Current Liabilities
- Three Financial Statements
- Three Financial Statement Model
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/accounting/balance-sheet/
0 Response to "The December 31 Balance Sheet of the Gemco Llp Reads as Follows."
Post a Comment